Discovering that your dog’s face is suddenly swollen can be alarming. This unexpected change often leaves pet owners scrambling for answers, wondering if the cause is minor or indicative of a more serious problem. While swelling can result from something as simple as an insect bite, it may also signal an allergic reaction, infection, or trauma—conditions that require immediate attention.

Understanding the potential causes and appropriate steps to take can make all the difference in your dog’s comfort and recovery. In this article, we’ll explore common reasons for facial swelling in dogs, provide guidance on first aid, and help you recognize when it’s time to seek professional veterinary care. By equipping yourself with this knowledge, you can respond effectively and ensure your beloved companion receives the care they need.
Let’s delve into what could be causing your dog’s swollen face and how you can take the best possible care of your furry friend.
1. Common Causes of Facial Swelling in Dogs
Facial swelling in dogs can arise from a variety of causes, ranging from mild allergic reactions to severe underlying health issues. Recognizing these potential causes is critical for determining the appropriate response. Below are some of the most common reasons why your dog’s face may swell, along with the symptoms to watch for.
1. Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions are a leading cause of sudden facial swelling in dogs. These can be triggered by:
- Insect bites or stings, such as from bees or spiders.
- Food allergies, often from proteins like chicken or beef.
- Environmental allergens, like pollen, mold, or chemicals.
Symptoms: Along with swelling, dogs may develop hives, redness, intense itching, and difficulty breathing in severe cases. Swelling is often most pronounced around the muzzle, eyes, or ears.
Example: A dog bitten by a bee may show rapid swelling of the face, coupled with pawing at the area and visible distress. Quick veterinary attention is crucial if the swelling worsens or breathing is affected.
2. Dental Problems
Oral health issues are another frequent cause of facial swelling, particularly in older dogs. Conditions like tooth abscesses, gum infections, or oral injuries can lead to localized swelling.
- Signs: Dogs with dental problems often exhibit drooling, bad breath, pawing at the face, or difficulty eating. Swelling is typically on one side of the face near the jaw.
- Example: A dog with a fractured tooth may develop an abscess, causing swelling that becomes painful over time. Dental radiographs and treatment, such as tooth extraction, may be required to resolve the issue.
3. Trauma or Injury
Accidents, such as falls, rough play, or fights with other animals, can result in facial swelling. This occurs due to bruising or soft tissue injuries.
- Indicators: Swelling from trauma is often accompanied by visible wounds, bruising, and behavioral changes, such as lethargy or reluctance to be touched.
- Example: A dog that collides with a sharp object during play may develop swelling at the point of impact, along with visible cuts or scrapes. Immediate first aid and monitoring for further complications, like infections, are essential.
4. Infections
Bacterial or fungal infections, such as cellulitis, sinus infections, or abscesses, can lead to significant facial swelling. These infections may originate from untreated wounds or underlying dental issues.
- Clues: Look for redness, warmth, and discharge from the swollen area. Dogs may also exhibit fever, loss of appetite, or lethargy in more severe cases.
- Example: A dog with cellulitis from a scratch might have a warm, swollen area that becomes increasingly tender. Antibiotics and proper wound care are needed to treat the infection effectively.
5. Serious Conditions
More severe causes of facial swelling include tumors, snake bites, or autoimmune diseases. These conditions can progress quickly and often require urgent veterinary attention.
- When to Worry: Signs of serious conditions include rapid swelling, systemic symptoms like vomiting or extreme lethargy, and noticeable lumps or growths in the swollen area.
- Example: A dog bitten by a snake may develop swelling that spreads rapidly, accompanied by pain, vomiting, or difficulty walking. Anti-venom treatment or emergency care is vital in such situations.
By identifying these common causes of facial swelling, pet owners can better assess the severity of the situation and take timely, appropriate action. If the swelling persists or worsens, seeking veterinary care is always the best course of action.

2. First Aid and Immediate Steps
When you notice that your dog’s face is swollen, acting quickly and calmly can make a significant difference. While some cases may resolve on their own, others require immediate intervention. Here’s how to handle the situation before professional care is available:
1. Stay Calm
Dogs are highly perceptive and can pick up on your emotions. If you appear stressed, your dog may become more anxious, potentially worsening their symptoms.
- Use a soothing tone and avoid sudden movements to keep your pet calm.
- Ensure a quiet, comfortable environment to reduce their stress levels.
2. Assess the Swelling
Take a closer look at your dog’s face to identify possible causes:
- Check for visible injuries, such as cuts, bruises, or puncture wounds.
- Look for bites or stingers from insects, which may be lodged in the skin.
- Observe for foreign objects that might be causing irritation.
If your dog is in pain or uncooperative, proceed gently and avoid forcing an examination.
3. Apply Initial Care
Based on your assessment, you can take these immediate steps:
- For trauma or injury: Use a cold compress wrapped in a cloth to reduce swelling. Apply for 10–15 minutes at a time, being cautious not to cause discomfort.
- For bites or stings: If safe to do so, gently remove the stinger with tweezers and clean the area with water. Avoid using household remedies unless instructed by a veterinarian.
- Medication caution: Do not administer over-the-counter medications like aspirin or ibuprofen without veterinary guidance, as these can be toxic to dogs.
4. Observe for Red Flags
Some symptoms indicate a more serious condition that needs immediate veterinary attention:
- Difficulty breathing or signs of distress.
- Inability to eat or drink, indicating discomfort or internal swelling.
- Swelling that spreads rapidly beyond the face or causes systemic symptoms like lethargy or vomiting.
5. Contact the Veterinarian
When in doubt, consult a veterinarian as soon as possible.
- Call for guidance: If the symptoms appear mild and your dog is otherwise behaving normally, a call to your vet may suffice to determine the next steps.
- Head to the clinic: For severe symptoms or signs of distress, go directly to an emergency clinic without delay.
By following these steps, you can provide your dog with immediate care and prepare for the next steps with your veterinarian. Acting quickly while keeping calm ensures your furry companion gets the attention they need.
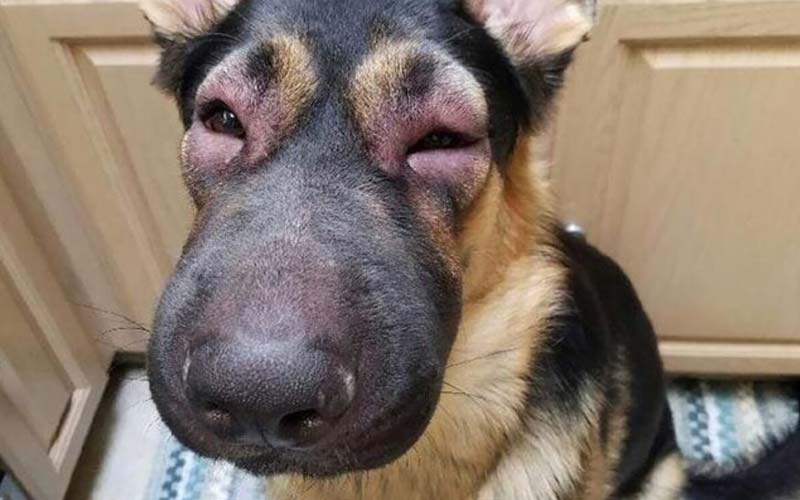
3. Diagnosing and Treating the Swelling
When your dog’s face is swollen, visiting a veterinarian is crucial to identify the cause and start appropriate treatment. Understanding the diagnostic process and treatment options can help you prepare for the visit and support your dog’s recovery effectively.
1. Diagnostic Steps
During the vet visit, several procedures may be conducted to pinpoint the cause of the swelling:
- Physical Examination: The vet will thoroughly inspect your dog’s face and body for signs of injury, infection, or abnormalities like growths.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays or ultrasounds may be used to check for underlying issues, such as dental problems, fractures, or tumors.
- Blood Tests: These can reveal infections, allergic reactions, or systemic diseases causing the swelling.
- Fine Needle Aspiration or Biopsy: If a lump or mass is present, a sample may be taken for further analysis.
This comprehensive evaluation ensures the cause is identified, leading to targeted treatment.
2. Possible Treatments
Once the cause of the swelling is determined, your vet may recommend one or more treatments based on the diagnosis:
Medications:
- Antibiotics to address bacterial infections.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to reduce swelling and discomfort.
- Antihistamines or steroids for allergic reactions.
Procedures:
- Abscess Draining: If the swelling is due to an abscess, the vet may drain it to relieve pressure and remove infected material.
- Dental Surgery: Severe dental issues, like abscessed teeth, may require tooth extraction or gum surgery.
- Tumor Removal: If a mass is identified, surgical removal and further testing may be needed to determine if it’s benign or malignant.
These treatments aim to resolve the swelling and address any underlying health problems.
3. Recovery and Aftercare
After treatment, proper care at home is essential for your dog’s recovery:
- Rest: Ensure your dog has a quiet and comfortable place to recover, free from stress or physical exertion.
- Diet Adjustments: Soft or modified foods may be necessary, especially after dental procedures.
- Follow-Up Visits: Schedule any recommended follow-ups to monitor healing and ensure the treatment is effective.
Be attentive to your dog’s behavior during recovery, and alert your vet if symptoms worsen or new issues arise.
By understanding the diagnostic and treatment process, you can work closely with your veterinarian to ensure the best outcome for your furry companion. Early intervention and diligent aftercare can help your dog return to their happy, healthy self.

4. Preventing Future Swelling Episodes
Taking proactive steps to maintain your dog’s overall health can reduce the risk of facial swelling. By focusing on regular care and being prepared for emergencies, you can help ensure your dog stays comfortable and healthy.
1. Routine Dental Hygiene
Good oral health prevents issues like gum infections and abscessed teeth, common causes of swelling.
- Brush your dog’s teeth with a vet-approved toothpaste several times a week.
- Offer dental chews or toys designed to reduce plaque and tartar buildup.
- Schedule professional cleanings with your veterinarian to address hard-to-reach areas.
2. Avoiding Allergens
Minimizing exposure to allergens can help prevent allergic reactions.
- Monitor your dog’s diet for potential food triggers, introducing new foods gradually.
- Reduce contact with environmental allergens such as pollen, dust, and chemical irritants.
- Use vet-recommended flea and tick preventatives to avoid bites that can cause swelling.
3. General Health Maintenance
Regular vet visits are crucial for catching potential issues early.
- Keep up with routine check-ups and vaccinations to protect against infections and diseases.
- Practice parasite prevention with medications for fleas, ticks, and heartworms.
4. Quick Action Plan
Being prepared for emergencies can make a big difference:
- Maintain an updated list of emergency contacts, including your regular vet and nearby emergency clinics.
- Keep a pet first-aid kit with essentials like sterile gauze, tweezers, and an ice pack.
By following these preventive measures, you can significantly lower the chances of future swelling episodes and keep your dog in excellent health. Proactive care not only addresses potential risks but also ensures your furry friend enjoys a happy, thriving life.

Conclusion
Facial swelling in dogs can be alarming, but with the right knowledge and swift action, most causes can be addressed effectively. We’ve explored the common causes of swelling, from allergic reactions and dental issues to trauma and infections, and the importance of seeking veterinary care. By staying calm, providing initial first aid, and following through with professional treatment, you can support your dog’s recovery.
To prevent future swelling episodes, maintaining routine dental hygiene, avoiding allergens, and staying on top of general health care are key. Regular veterinary check-ups and being prepared for emergencies can further safeguard your pet’s well-being.
If your dog experiences swelling, don’t hesitate to reach out to your veterinarian. Early intervention is crucial to preventing more serious complications. With proactive care and a quick response, you can help ensure your furry companion leads a healthy, comfortable life.
If you’re concerned about your dog’s swelling or want guidance on preventive measures, schedule a vet visit today. Your prompt attention can make all the difference in your dog’s health and happiness.